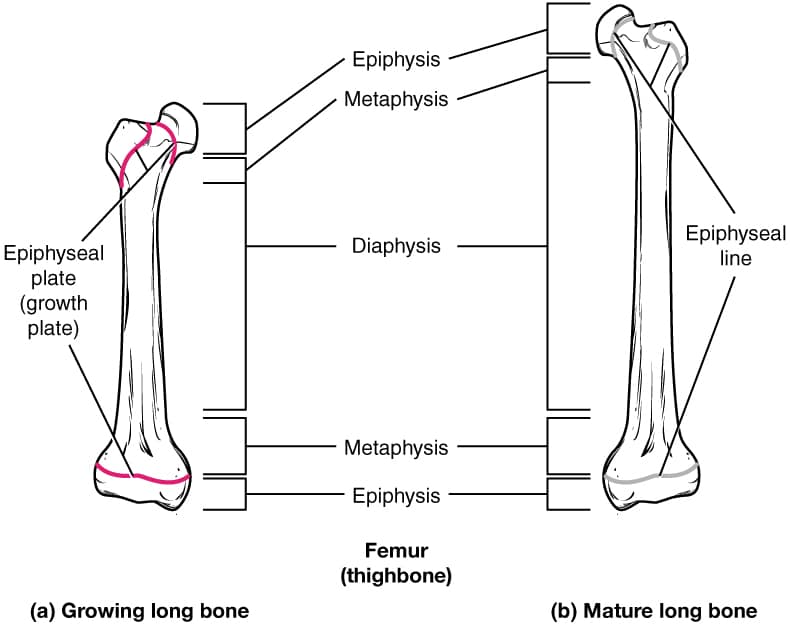
The growth plate anatomy and disorders Biology Diagrams Function. The main function of the epiphyseal plate is to allow for growth and development of long bones in children and adolescents. [5] It does this through the process of endochondral ossification, in which chondrocytes in the proliferative zone actively divide and produce new cartilage tissue. [4] This tissue is then replaced by bone tissue as the chondrocytes in the degenerative zone die The growth plate is the cartilaginous portion of long bones where the longitudinal growth of the bone takes place. This figure is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license from Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site. Ultrastructural localization of collagen types II, IX, and XI in the

The growth plate is a key component of developing bones. The growth plate, or physis, is a highly ordered structure and is composed of discrete layers. Each layer has a specific function that contributes to the growing bone. The anatomy and disorders of the growth plate is also a common basic science viva topic in the FRCS examination. The
PDF The Growth Plate: Anatomy and Injuries Biology Diagrams
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th ed.). Pearson. ISBN 978-0134760239. Hall, J. E. (2020). Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology (14th ed.). Elsevier. The epiphyseal plate, also known as the growth plate or physis, is a hyaline cartilage plate located at the ends of long bones in children and adolescents. It is the site where new Longitudinal growth of the skeleton is a result of endochondral ossification that occurs at the growth plate. Through a sequential process of cell proliferation, extracellular matrix synthesis, cellular hypertrophy, matrix mineralization, vascular invasion, and eventually apoptosis, the cartilage model is continually replaced by bone as length increases. Longitudinal growth of the skeleton is a result of endochondral ossification that occurs at the growth plate. Through a sequential process of cell proliferation, extracellular matrix synthesis, cellular hypertrophy, matrix mineralization, vascular invasion, and eventually apoptosis, the cartilage model is continually replaced by bone as length increases.

The growth plate is a key component of developing bones. The growth plate, or physis, is a highly ordered structure and is composed of discrete layers.Each layer has a specific function that contributes to the growing bone. As a result of this, each layer also has the potential for problems to occur, leading to recognized diseases and syndromes.

Location, Structure, Function, Anatomy Biology Diagrams
Growth Plate Anatomy - See: - Enchondral Ossification - Limb Development - Growth Deformities of the Limbs - Pediatric Bone Circulation - Physeal Bone Bridge - Salter Harris Classification - Undifferentiated or Resting Cartilage Cells: - immediately adjacent to epiphysis are irregularly scattered cartilage cells, called the resting cell zone;
