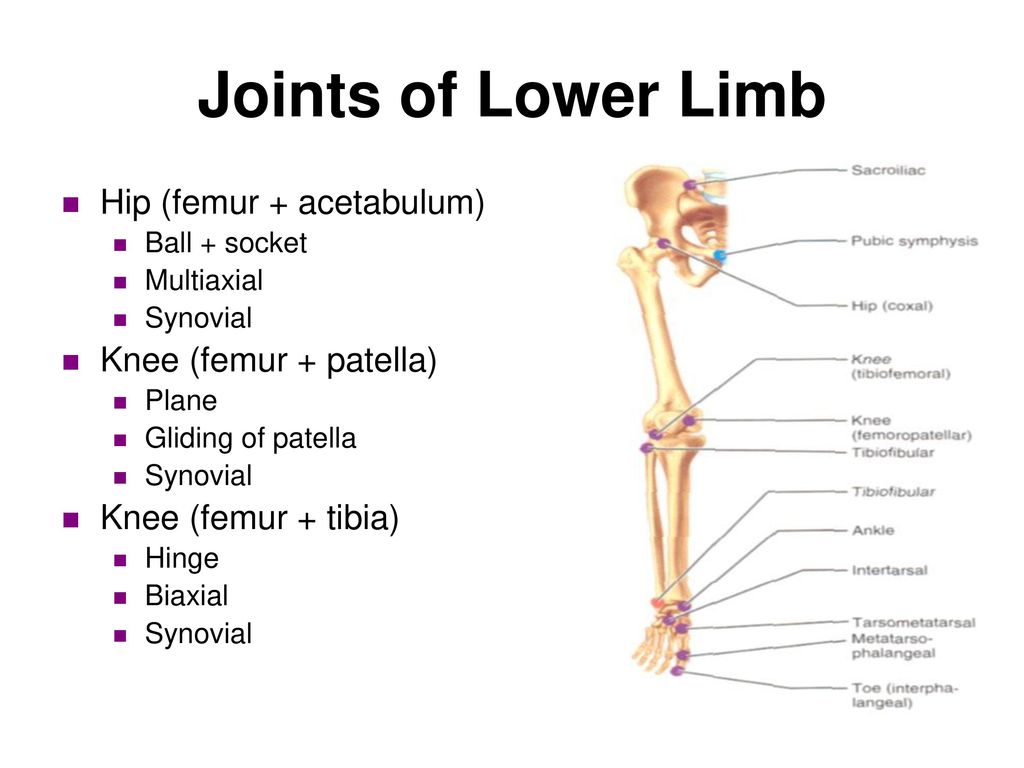
Joints of lower limb Biology Diagrams Lower limb anatomy Author: Adrian Rad, BSc (Hons) • Reviewer: Nicola McLaren, MSc Last reviewed: September 11, 2023 Reading time: 21 minutes Recommended video: Regions of the lower limb [20:39] Like any structure in the human body, the knee also requires a neurovasculature supply.
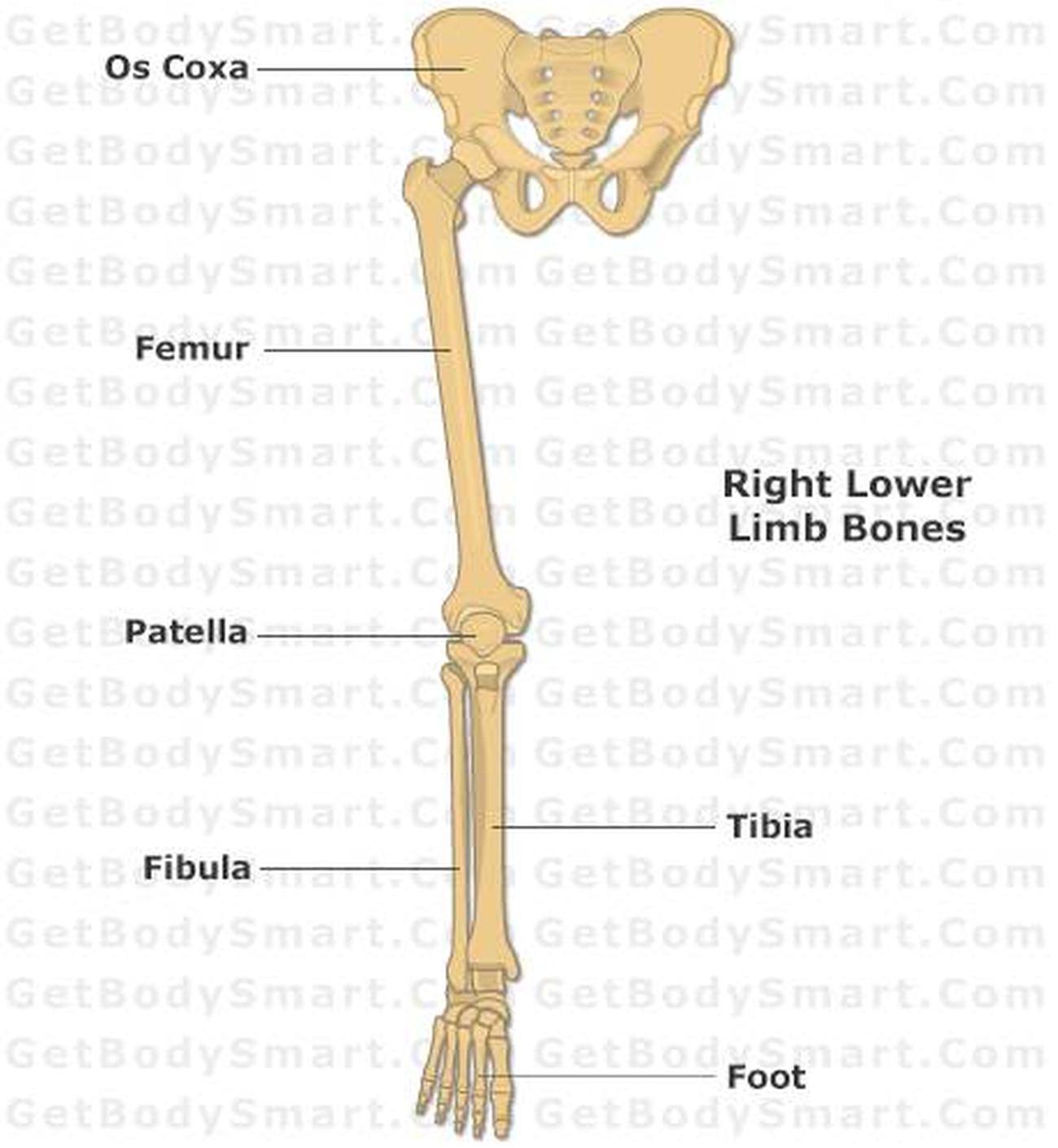
3D interactive models and tutorials on the anatomy of the lower limb, including the muscular compartments, osseus structures, blood supply and innervation. Our upper limbs are free, mobile, and adapted for prehension. Each articulates with the trunk at the sternoclavicular joint. Our lower limbs have to bear the weight of the body when walking, runnning, jumping, or standing. They are united behind to the vertebral column at the sacroiliac joints and in front to each other at the symphysis pubis. 12 Bones of the Lower Limb Bones of the Lower Limb. For reference, the figure below shows how all the bones of the lower limb fit together. Anterior view of the arrangement of bones in the pelvis and leg. Figure 6.1 in Human Anatomy, Color Atlas and Textbook by J.A. Gosling et al., 6 th edition (2017).
Human anatomy: Definition and overview of the organs Biology Diagrams
Regional anatomy organizes the body into several body parts or regions: upper limbs, lower limbs, trunk (thorax, abdomen, pelvis, back), head, and neck. This approach divides teaching and learning into discrete regional didactic areas, each one containing its respective bones, joints , muscles, arteries, veins, nerves, lymphatics, and organs. The hand is a very mobile part of the upper limb, and we perform very specialised tasks with it every day, key adaptations can be seen in the specialised structures of the hand. In this section, learn more about the upper limb: Its bones, muscles, nerves, joints, blood vessels and lymphatics, anatomical areas, and structures found in the hand. Lymphatic Drainage of the Lower Limb; Venous Drainage of the Lower Limb +1 more; Other. The Arches of the Foot; Walking and Gaits; Popular. Encyclopaedia The Middle Cranial Fossa. by Briony Adams. TeachMeAnatomy. Part of the TeachMe Series. The medical information on this site is provided as an information resource only, and is not to be
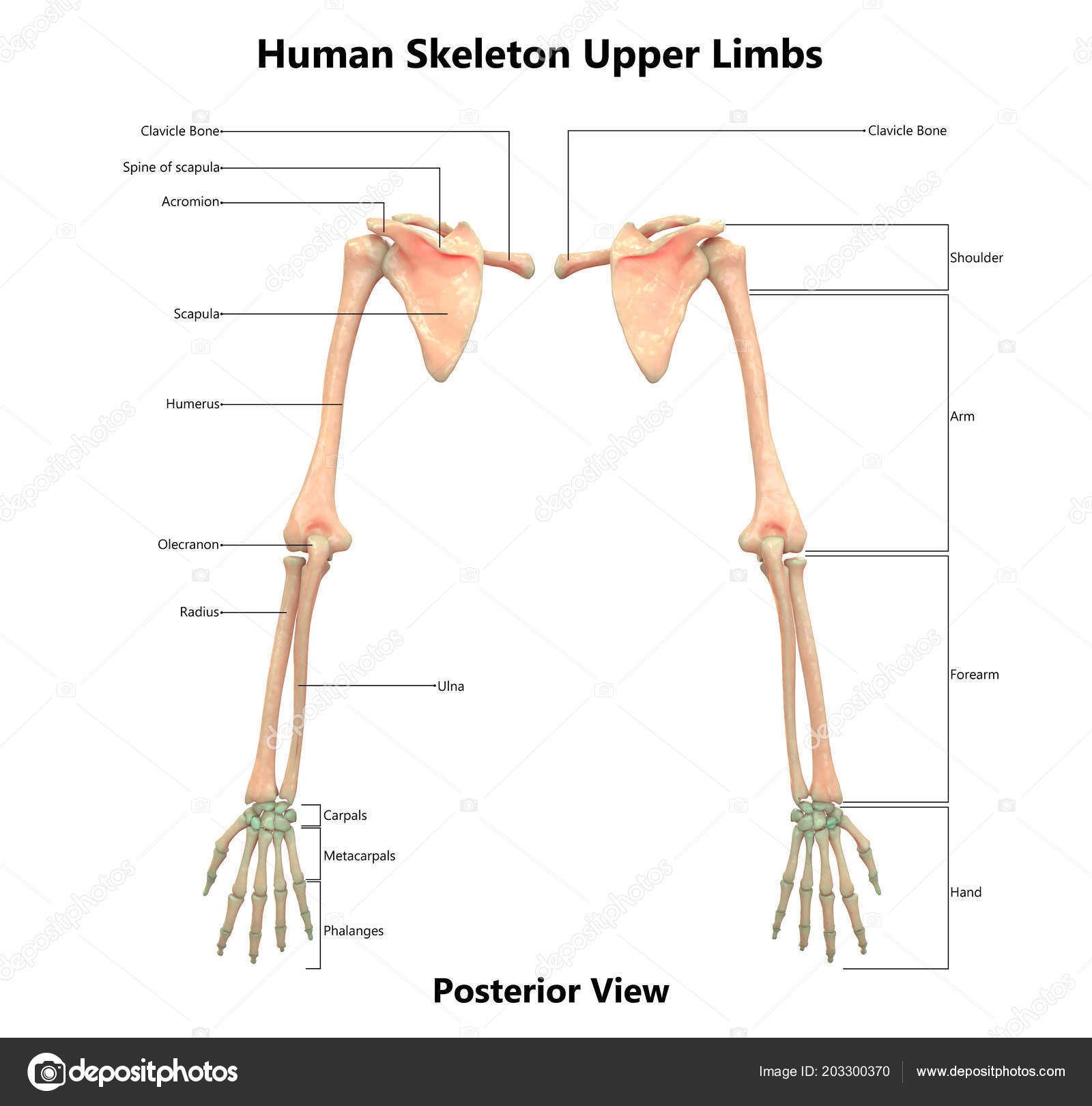
The upper extremity or arm is a functional unit of the upper body. It consists of three sections: the upper arm, forearm, and hand. It extends from the shoulder joint to the fingers and contains 30 bones. It also consists of many nerves, blood vessels (arteries and veins), and muscles. The nerves of the arm are supplied by one of the two major nerve plexus of the human body, the brachial plexus. Aquatic and semiaquatic tetrapods usually have limb features (such as webbings) adapted to better provide propulsion in water, while marine mammals and sea turtles have convergently evolved flattened, paddle-like limbs known as flippers. In human anatomy, the upper and lower limbs are commonly known as the arms and legs respectively, although
