How a warming world is a threat to our food supplies Biology Diagrams It may seem that the impact of species loss on humans is negligible; however, species loss affects entire ecosystems especially if there are missing components from food chains. Without predators to eliminate fast producing prey, some species quickly become invasive and disrupt the foundations of an ecosystem. When the food chain is disrupted, the effects can reverberate through the entire ecosystem, with potential risks to biodiversity, human health, and economic stability. Legal protection of endangered species and their habitats can also help mitigate the effects of disruption. Moreover, promoting biodiversity through sustainable agricultural
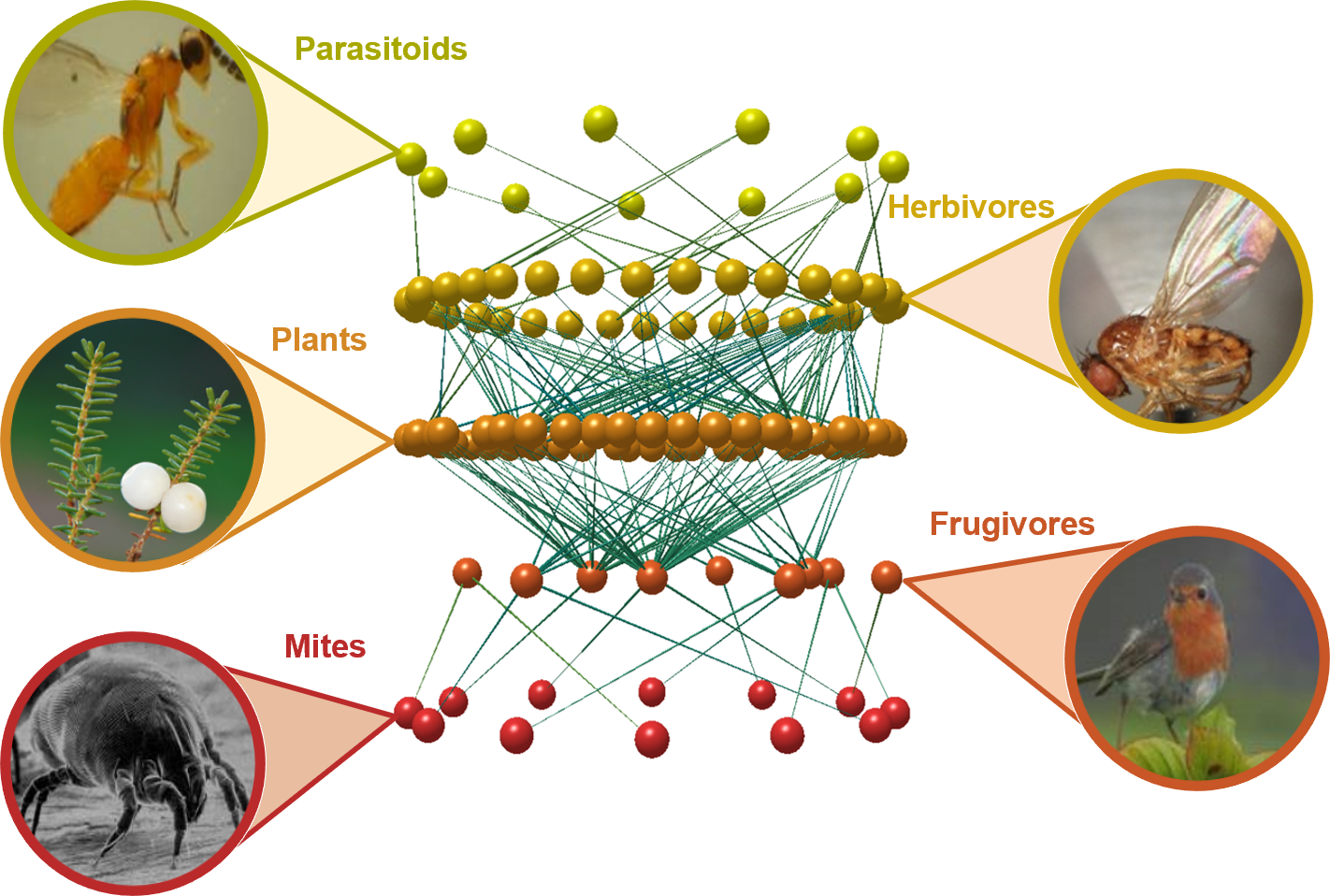
Species belonging to the three fauna that occupy different locations in the food chain of stream ecosystems (i.e., fish, benthic macroinvertebrates, and epilithic diatoms) were investigated and taxonomically resolved at the species level; for instance, fish were surveyed for all habitat types including riffle, pool, and run, using kick-net
Endangered Species and Ecosystems Biology Diagrams
Disrupted Habitat. Extinction of animal or bird species in the food chain may alter the physical environment as well. For instance, accidental introduction of the predatory brown tree snake to Guam wiped out 10 of the 12 native bird species on the island causing collateral damage to the forest, according to a University of Washington study.

A food web is comprised of all the connections between predators and their prey in a given region. Complex food webs are essential for managing populations in a manner that allows more species to coexist, hence promoting the biodiversity and stability of ecosystems. But animal losses may diminish this complexity, thereby reducing the resilience This is worrying from the point of view of sustainability, food security, biodiversity and health. Our food systems, nutrition, health, clean air, climate, and freshwater depend on biodiversity and healthy ecosystems—an interdependent web of animal, plant, fungal and bacterial life. For instance, without pollinators—insects, birds and other

Scientists' warning on endangered food webs Biology Diagrams
Species like polar bears and sea turtles are losing critical breeding and feeding grounds. Changing Ecosystems. Warming temperatures force animals and plants to migrate to cooler areas. Some adapt, but others face extinction when they can't keep up. Coral reefs, for instance, are dying from ocean warming and acidification. Disrupted Food Chains
Generally, endangered species interact more broadly than extant non-endangered species (fig. S1C; F 1,3765 = 19.0, P << 0.0001), indicating their greater structural importance within food webs. Across regions, endangered species extinction would cause 10% to 67% further reductions in participating species and 15% to 80% in links beyond that The strong body of knowledge accumulated in recent decades has shown that endangered species lists are only the most visible side of a more insidious kind of threat cast over the natural food webs that support life on Earth (Memmott, 2009; Tylianakis et al., 2010; Valiente-Banuet et al., 2015).

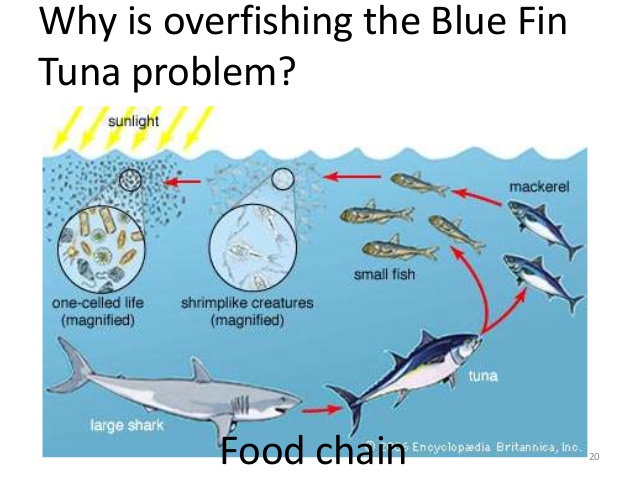
How Overfishing Disrupts Marine Ecosystems And Food Chains Biology Diagrams
Explore how overfishing disrupts marine ecosystems and food chains, affecting biodiversity, fisheries, and the balance of oceanic life. and when this balance is disrupted, Conservation efforts aim to protect endangered species and restore the balance of marine ecosystems. These initiatives are essential for the long-term sustainability
