Cell Growth and Division Biology Diagrams The process of programmed cell death, or apoptosis, is generally characterized by distinct morphological characteristics and energy-dependent biochemical mechanisms. Certain forms of human B cell lymphoma have overexpression of Bcl-2, and this is one of the first and strongest lines of evidence that failure of cell death contributes to Anatomy and Physiology. Stages of Apoptosis: Detailed Steps in Programmed Cell Death. Explore the key stages of apoptosis, from initiation to clearance, and understand how programmed cell death maintains balance in biological systems. Though both apoptosis and necrosis result in cell death, their mechanisms and consequences differ

Regulated cell death mediated by dedicated molecular machines, known as programmed cell death, plays important roles in health and disease. Apoptosis, necroptosis and pyroptosis are three such
Definition, Pathways, Assay, Examples (vs Necrosis) Biology Diagrams
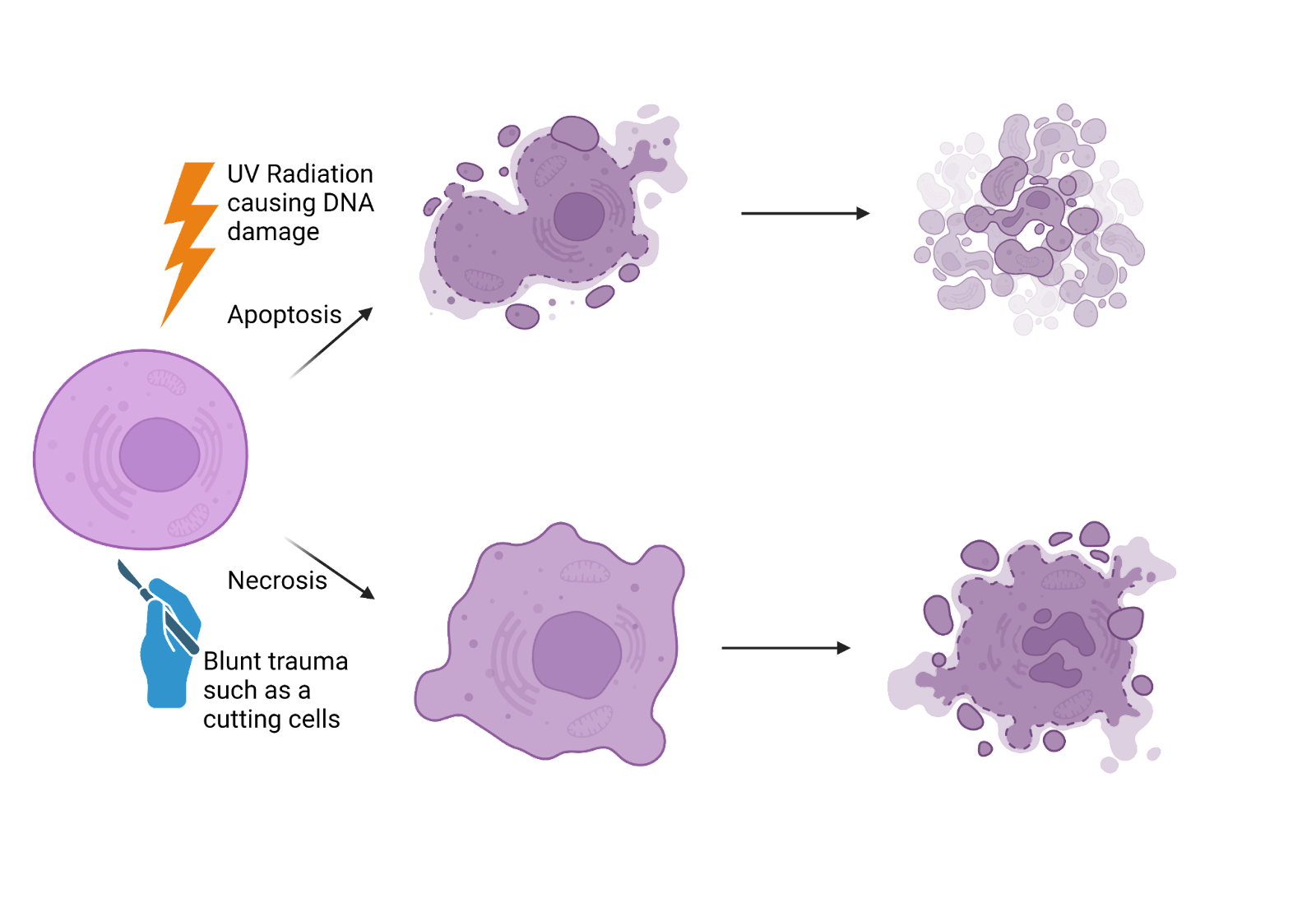
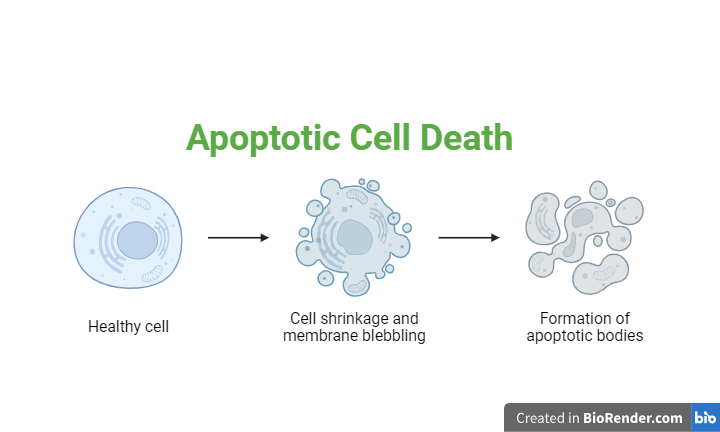
First identified in the 1970s, apoptosis was considered parallel to mitosis. Many years later, apoptosis is defined as the ATP-dependent, enzyme-mediated, genetically programmed death of cells that are either no longer required or pose a threat to the organism. Apoptosis results when the cytoskeleton (by proteases) and DNA (by endonucleases) break down through several pathways that are Apoptosis is referred to as "programmed" cell death because it happens due to biochemical instructions in the cell's DNA; this is opposed to the process of "necrosis," when a cell dies due to outside trauma or deprivation. During the early development of the human nervous system, huge numbers of cells die through apoptosis. Why

Cell death, like apoptosis and autophagy, are natural processes. Cells die or recycle to make way for newer, more efficient ones. Experts believe that healthy human cells can replicate or divide up to 60 times before cell death occurs. Your body is constantly making new cells to replace damaged and dying ones. Advertisement.
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology Biology Diagrams
Today, however, apoptosis is implicated in biological processes ranging from embryogenesis to ageing, from normal tissue homoeostasis to many human diseases, and it has become one of the hottest fields of biomedical research. Summary points. Apoptosis is a genetically regulated form of cell death In adult animals apoptosis is used to remove cells that have become a threat to survival. Such cells can include cancer cells or cells that are infected with bacteria or a virus.Apoptosis also removes cells that are normal but no longer needed, such as cells that produce antibodies after the need for the antibody has passed. Apoptosis can also be triggered in otherwise normal cells by external It results in the death of 50 to 70 billion cells per day in an average adult human being. It is also termed as 'cellular suicide' as cells undergo a highly regulated process for the programmed removal of cells from the body. and chemical-induced cell death. Apoptosis is a part of development as it is essential in the differentiation of
